Oracle plan_table contains detailed information about the execution plan. It is a temporary table that holds the output of the query plan. Oracle plan_table is created to describe different types of information that help to understand a query’s execution behavior.
Explain plan is a great tool for finding the path of query Execution. The execution plan shows much information by looking at tree structure and other referring information.
Execution plan Information
- Execution order of an SQL statement by Oracle optimizer.
- Join methods when joining the table.
- Filter, order, sorting, or aggregation operation information.
- Operation Cost, Cardinality, Byte, Time, and other operation-related information
- Partitioning and parallel execution distribution
- Index Scanning methods like Range, Skip, Unique, etc.
- Table join order
- Table Join method (Hash Join)
- Data operations like Filter, Sort, aggregations, etc
Each execution plan flows by doing one of the specified tasks related to gathering the data. When considering a single flow each flow has a specific weight when execution time. Weight can be shown by using properties in the Oracle plan_table.
Oracle plan_table columns are used to identify the resources used by the query in each step. Each step has some weight and also some columns use to see which resources use to complete each flow. By looking at the values in each column in the Oracle plan_table it is easy to identify what happens or how it happens when executing the flow.
Oracle PLAN TABLE Columns (Important)
The below image shows what type of information is available on the Explain Plan. Cost, Cardinality, Bytes, Filter predicates, Optimizer, and Object names are important.
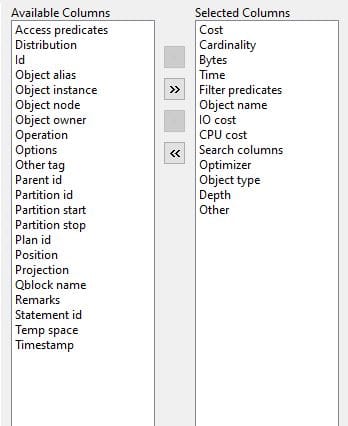
Oracle PLAN_TABLE Columns
oracle plan_table has a lot of columns, but all are not useful all the time. As I mentioned above some of the columns are very helpful when improving performance in a query.
oracle plan table below columns are heavily used on performance improvement and also can be used to see which resources are used by each step As an example weather query used one of the scan types to fetch records from a table.
explain plan table also helps to find what type of data processing type used to filter the data. Below are some of the data processing ways that are used to merge tables in a faster way.
- Hash Join
- Nested loop
- Sort Merge
The execution plan contains other properties as well but we can see what resources are used by them also what the weight or hardness of that step
- Order by
- Sort
- Filtering
- Groping
- Full table scans or weather able to use or create an index
Finally, these all kinds of features can be used to improve the performance of a query lets see what kind of columns are available in Oracle plan_table. Red color ones might important
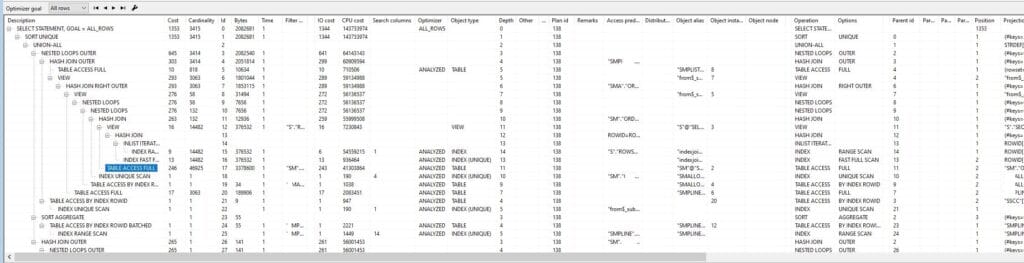
Explain plan table
| Column name | Data type | Description and what information could see | Example |
| STATEMENT_ID | VARCHAR2 | Unique ID of a plan | USER |
| PLAN_ID | NUMBER | Who owns this table view r index | 133 |
| TIMESTAMP | DATE | Date and time of generated EXPLAIN PLAN | 10/20/2024 7:55:07 AM |
| REMARKS | VARCHAR2 | This is used to add some comments the weather profile. | |
| OPERATION | VARCHAR2 | What does the operation execute in this step | INDEX |
| OPTIONS | VARCHAR2(255) | A variation on the operation described in the OPERATION column | UNIQUE SCAN |
| OBJECT_NODE | VARCHAR2(128) | EXPLAIN PLAN statement referring to ID | |
| OBJECT_OWNER | VARCHAR2(128) | Link to the object name | Owner |
| OBJECT_NAME | VARCHAR2(128) | Name of the used object this can be a table name or view name. | Department Table |
| OBJECT_ALIAS | VARCHAR2(261) | ID of the next execution step. this is a link with the ID column which is next | SO”@”SEL$2 |
| OBJECT_INSTANCE | NUMBER(38) | Unique alias of a table or view. Normally we use alias t refer table when using multiple tables with join | 1 |
| OBJECT_TYPE | VARCHAR2(30) | Information about the object. It can be a TABLE or INDEX or Other for example, NON-UNIQUE for indexes | INDEX (UNIQUE) |
| OPTIMIZER | VARCHAR2(255) | Currently Running State of the optimizer | ANALYZED |
| SEARCH_COLUMNS | NUMBER | 3 | |
| ID | NUMBER(38) | Number to identify each step that is added when generating the execution plan | 3 |
| PARENT_ID | NUMBER(38) | This is the first row of output; position indicates the Oracle optimizer’s estimated cost of step. For the other rows, this shows the position relative to the other children of the same parent. | |
| DEPTH | NUMBER(38) | position of the object appears in the original statement | 2 |
| POSITION | NUMBER(38) | This is an important column showing the weight of the operation there are no measurements but the value indicates how much heavy processes happening in this step The value of this column is a function of the CPU_COST and IO_COST columns. | 2 |
| COST | NUMBER(38) | explain the contents of the OTHER column: SERIAL – Serial execution. SERIAL_FROM_REMOTE – Serial execution from a remote site. PARALLEL_FROM_SERIAL – Serial execution. Output: partitioned or parallel execution. PARALLEL_TO_SERIAL – Parallel execution. Output: Serial query. PARALLEL_TO_PARALLEL – Parallel execution. Output: parallel execution. | 2131 |
| CARDINALITY | NUMBER(38) | Estimated number of rows accessed by the operation | 234555 |
| BYTES | NUMBER(38) | Estimated number of bytes accessed by the operation | 123123123 |
| OTHER_TAG | VARCHAR2(255) | Temporary space (in bytes) is used when merging or other type of operations. In those cases, all the time not able to execute queries in memory in such cases use Temp Space | |
| PARTITION_START | VARCHAR2(255) | Stop partition of a range of accessed partitions: number – compiler identified Start partition NUMBER for partition number KEY – partitioning key values when Start partition INVALID – Used partitions that are empty | |
| PARTITION_STOP | VARCHAR2(255) | Stop partition of a range of accessed partitions: number – compiler identified Start partition NUMBER for partition number KEY – partitioning key values when Start partition INVALID – Used partitions that is empty | |
| PARTITION_ID | NUMBER(38) | Values for PARTITION_START and PARTITION_STOP columns | |
| OTHER | LONG | I/O cost is a number of data blocks read by the operation. There are Io calls when retrieving data from a database. Actually, when reading a data block | |
| DISTRIBUTION | VARCHAR2(30) | ||
| CPU_COST | NUMBER(38) | Reference to OTHER_TAG column that shows the identified step when the process executing | 123 |
| IO_COST | NUMBER(38) | Start partition of series of the partitions: number – compiler identified Start partition NUMBER for partition number KEY – partitioning key values when Start partition INVALID – Used partitions that are empty | 321 |
| TEMP_SPACE | NUMBER(38) | CPU cost is the number of machine cycles required for the operation. This is how heavy when executing the CPU. | |
| ACCESS_PREDICATES | VARCHAR2(4000) | When accessing data predicates are used to find the start and end position using an index range scan or other scanning types. | |
| FILTER_PREDICATES | VARCHAR2(4000) | When accessing data predicates used to find the start and end position using an index range scan or other scanning types. | “SMPLINE”.”QTY_ASSIGNED”>0 |
| PROJECTION | VARCHAR2(4000) | What is the level of the tree structure? position of the structure | |
| TIME | NUMBER(38) | Elapsed time (in seconds). | 2 |
| QBLOCK_NAME | VARCHAR2(128) | Name of the query block | SEL$5DA710D3 |
Summary
oracle plan_table is generated for executing a plan. That helps t find what are the steps that used when executing a query. This is also helping to find what are the steps that can improve performance.
explain plan table in Oracle has a lot of columns that show different values related to each step that can be measurement value, resources used, or any their property that need to execute the query. oracle explain plan table columns giving a full picture of queries that execute in the current database.
Ref: Oracle DOC


